[ Java ][HackerRank] 30 Days of code Day 9
in Algorithm
Day 9: Recursion 3 (재귀)
해커랭크 튜토리얼을 번역했습니다
이것은 문제를 두 부분(기본 케이스와 재귀 케이스)으로 나누는것을 포함하는 알고리즘 개념입니다.
문제는 더 작은 부수문제로 나뉘어집니다.
기본 케이스에서 만나게 될때, 각각의 부수문제를 위한 해결책은 합쳐지고 그것들의 결과는 전체문제의 정답으로 도출되어집니다.
만약 기본케이스에서 만나지 못하면, 함수의 재귀케이스들은 다시 함수를 불러서 값을 수정합니다.
코드는 반드시 기본케이스가 몇개의 숫자의 반복 이후에도 도달 할 수 있는 방식으로 구조화되어있어야하며,
이것은 이후에 변경된 각각의 값은 기본케이스에 점점 더 가까워질 수 있도록 도와주어야 한다는 뜻입니다.
그렇지 않을경우, 당신은 무한 루프에 빠지게 될 것입니다
아래의 코드를 봐주세요:
// Multiply 'n' by 'k' using addition:
private static int nTimesK(int n, int k) {
System.out.println("n: " + n);
// Recursive Case
if(n > 1) {
return k + nTimesK(n - 1, k);
}
// Base Case n = 1
else {
return k;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = nTimesK(4, 4);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
}
이 코드를 실행하면,
n: 4
n: 3
n: 2
n: 1
Result: 16
우리는 이런 값을 도출할 수 있습니다.
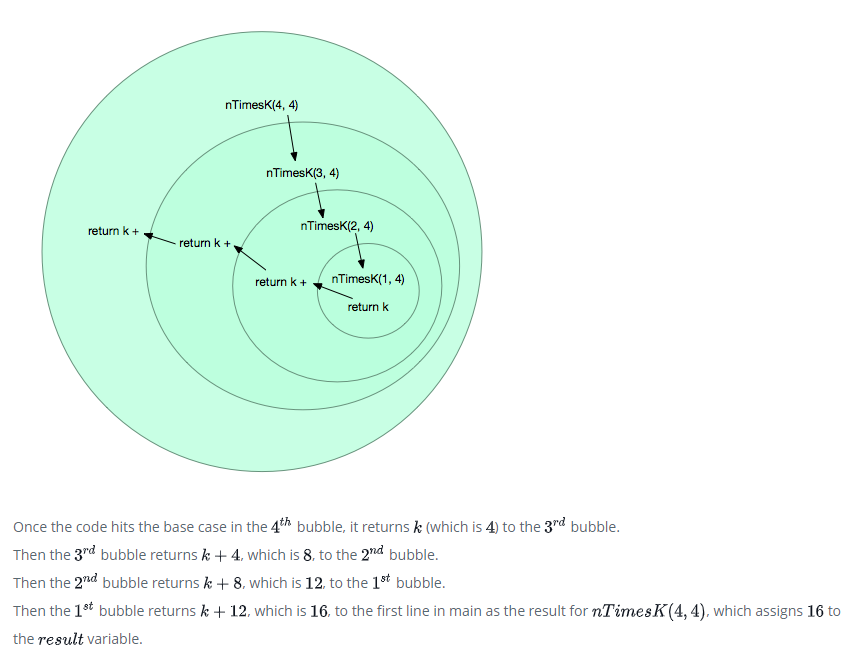
아래의 다이아그램은 위의 코드를 묘사하고 있습니다. nTimesK를 부를때마다 매번 원으로 나타나게 되며,
각각의 새로운 재귀호출 원은 안에 쌓입니다. 그리고 최상단의 원은 그것을 부르는 책임을 가지고 있습니다.
함수는 재귀적으로 기본케이스(n이 1일때)에 도달할때까지 값을 없애가면서 스스로를 호출합니다.
기본케이스에 도착할때, 이것은 기본케이스의 리턴값(k=4)을 원안에 통과시키고 최종 결과에 도달할때까지
계속해서 k+이전의 리턴 값을 통과시킵니다
Task Write a factorial function that takes a positive integer, as a parameter and prints the result of ( factorial).
Note: If you fail to use recursion or fail to name your recursive function factorial or Factorial, you will get a score of .
Input Format
A single integer, N(the argument to pass to factorial).
Constraints
- 2 <= N <= 12
- Your submission must contain a recursive function named factorial.
Output Format
Print a single integer denoting N! .
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.security.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Solution {
// Complete the factorial function below.
static int factorial(int n) {
if(n == 1){
return n;
}else{
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
}
private static final Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(System.getenv("OUTPUT_PATH")));
int n = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.skip("(\r\n|[\n\r\u2028\u2029\u0085])?");
int result = factorial(n);
bufferedWriter.write(String.valueOf(result));
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.close();
scanner.close();
}
}
n이 기본값인 1이면, n을 반환하고
n이 n이 아니면, n _ (n-1) _ (n-2) … 로 반환해야하기 때문!
